Sun Skin Care Advice
Who can resist the sense of well-being that comes with exposure to the hot summer sun. Even in the dead of winter, the sun warms the body and soul, bringing back childhood memories of vacations spent playing in the sand—without sunscreen!
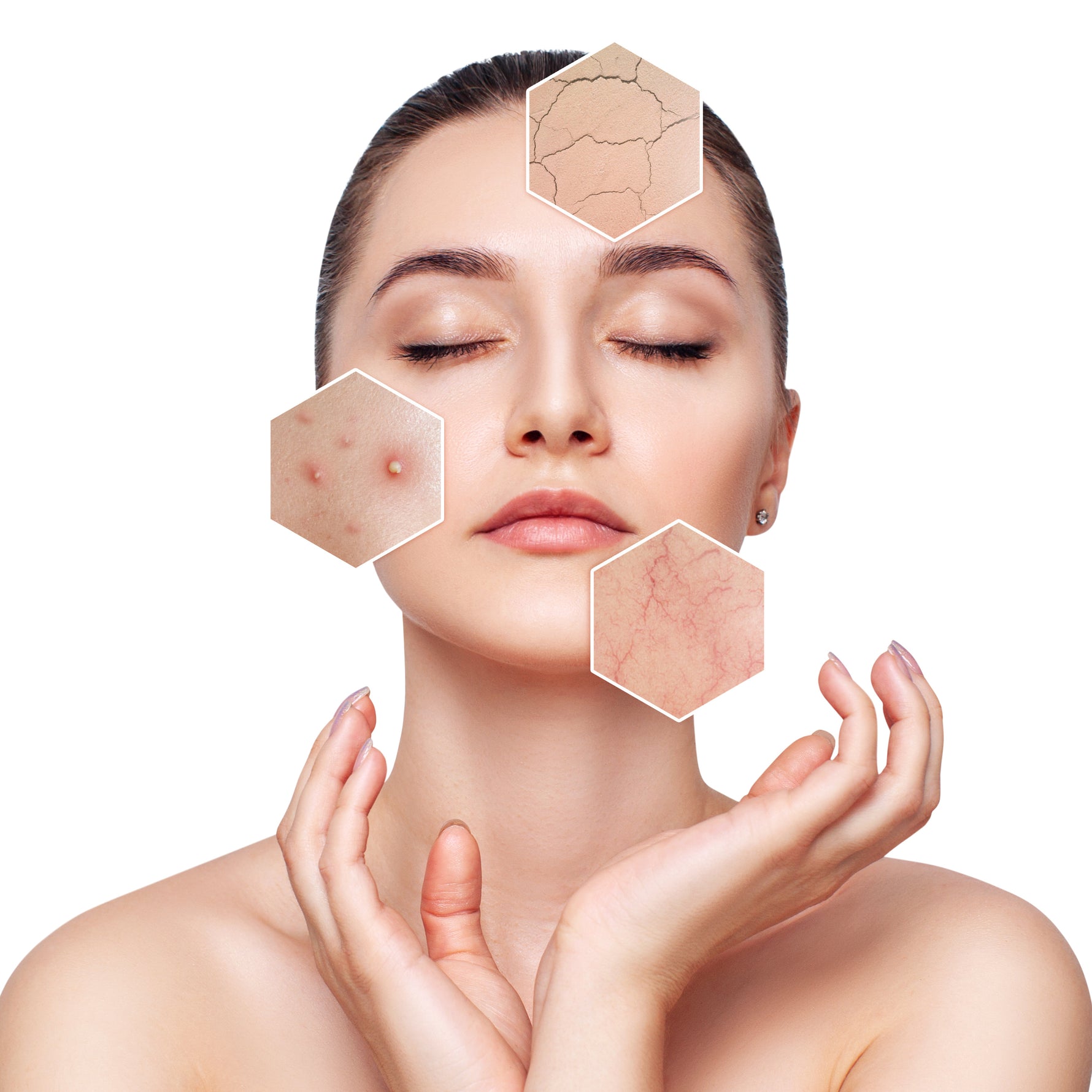
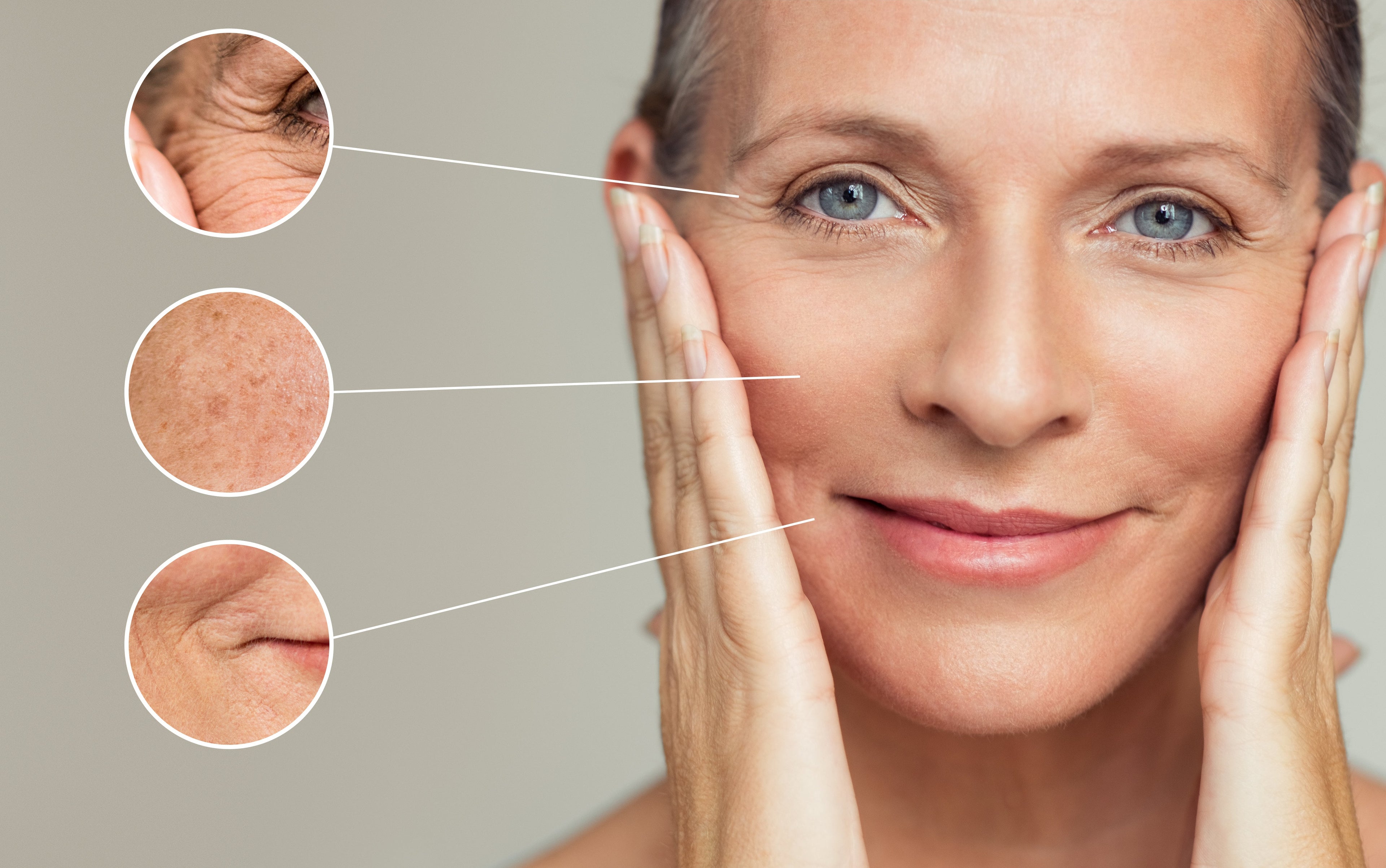
Although it can be a source of pleasure—and vitamin D, which promotes the absorption of calcium—the sun also has harmful effects. From painful sunburns to age spots, deep wrinkles and even cancerous tumours, the sun’s effects worsen over time.
You’re likely familiar with two of the more common sun-induced changes to your skin—suntan and sunburn. But what you may not know is that darkening and reddening of the skin are among the first signs of skin damage.
How the sun damages the skin
Every day, significant amounts of solar radiation reach the Earth’s surface in the form of visible and invisible ultraviolet (UV) rays. Although invisible UV rays account for only 5% of the radiation (the remaining 95% being visible light and infrared rays), they are largely responsible for skin damage.
Most of the ultraviolet rays are blocked by the ozone layer of the stratosphere (30,000—60,000 feet above sea level). These include short waveband UVC rays and large amounts of UVB rays. UVA, on the other hand, is not blocked by the ozone layer and reaches the surface of the earth in large amounts.
Although UVA radiation has less energy than UVB radiation, it penetrates deeper into the skin, causing it to deteriorate and age prematurely. Unlike high-intensity UVB radiation which causes skin to redden, UVA offers no visible warning signs of its harmful effects on the skin. Recent studies have shown that chronic exposure to UVA can cause damage to the collagen and elastic fibres which give skin its shape, definition and suppleness, thus causing wrinkling and, over time, premature skin aging.
UVB radiation is the most active in terms of producing redness, and is also referred to as sunburn radiation. UVB significantly decreases the levels of the skin’s natural antioxidants (vitamin E, vitamin C), thus impairing the skin’s ability to protect itself against free radicals. Free radicals are active molecules which can damage cells and tissues and are generated by exposure to sunlight. UVB is thought to be a potential cause of skin cancer due to the DNA damage
it causes.
Characteristics of different types of radiation
|
How to protect your skin
Although the dangers of sun exposure have been well documented, the vanity of having a deep tan continues to represent health and wealth in the minds of many teens and adults. Unfortunately, there has been a lack of urgency concerning prevention of skin damage due to sun exposure among most age groups. This is because it takes decades before skin aging becomes apparent to the naked eye in the form of deep wrinkles, age spots and leathery skin.
Many of the sun care products marketed around the world contain UVB filters and thus provide adequate protection against the reddening effects of UVB rays. The protective effects of such products are rated by their SPF values (Sun Protection Factor). The higher the SPF, the better protection it provides against UVB light. Unfortunately, such products provide a false sense of protection and actually encourage sun worshippers to spend more time outdoors.
Some products also provide protection against the shorter UVA wavelengths (UVA II: 320—340 nm), but they do not protect against the longer UVA wavelengths (UVA I: 340—400 nm), which penetrate much deeper into the skin, causing formation of fine lines, wrinkles and other damage. When combined with UVB filters, a broad-spectrum UVA filter such as Parsol 1789 used in all Reversa UV formulations, provides protection against the entire spectrum of UVB and UVA, thus protecting against the formation of fine lines, wrinkles, age spots and skin damage in general.
If you want to keep your skin looking and feeling healthy and young, here’s a short list of helpful tips:
- Protect yourself against daily sun damage by applying sunscreen prior to sun exposure, even indoors. Whether you’re driving to work or just sitting by a window, you’re still exposed to harmful UV rays.
- Stay out of direct sunlight and seek out a shady spot whenever you can. Wear a hat, UV-blocking sunglasses and clothing that protect your entire body.
-
Avoid the afternoon sun. Steer clear of the sun between 10 a.m. and
4 p.m. to limit the damaging effects of solar UV rays. -
Avoid tanning, both outdoors and indoors under artificial UV light.
Your skin will thank you later. -
Schedule an appointment with your dermatologist for expert advice on how to better take care of your skin and identify
any unusual changes to it. - If you use rejuvenating skin care products with glycolic acid and an SPF value, make sure they contain the broad-spectrum UVA filter Parsol 1789 and UVB sun filters. In addition to providing effective anti-aging properties and hydration, they will protect your skin from the sun’s harmful rays and help maintain your skin’s youthful appearance.
The following Reversa products contain broad-spectrum UV protection with Parsol 1789:
- Anti-Wrinkle Cream SPF 15
- Anti-Wrinkle Cream SPF 30
- Anti-Wrinkle Eye Contour Cream SPF 15
- Radiance Cream SPF 30
- Urban Protection Hydrating Care SPF 30
Share